
No More Keywords for Math Word Problems
The use of math keywords focuses on looking at the words of a word problem in isolation and not in the context of the problem. In this post, I share four reasons why using keywords for math word problems fail students.
There are 125 sheep and 5 dogs in a flock. How old is the shepherd?
1st Student: “I can’t solve this because it doesn’t say anything about the shepherd.”
2nd Student: “120 years old because 125 minus the 5 dogs in a flock.”
3rd Student: “25.” [The student’s work shows 125 divided by 5].
4th Student: “25” [The student’s work shows 125 divided by 5].
5th Student: “25” [The student’s work shows 125 divided by 5].
6th Student: “It doesn’t tell you.”
7th Student: “130” [The student’s work shows the sum of 125 and 5.]
8th Student: “65” [The student’s work shows (125 + 5) ÷ 2.]
9th Student: “25.” When asked to explain her solution, the student responded, “Because it doesn’t say the difference, or the sum, or the product.”
Of the 32 eighth-grade students asked to solve this problem, only 8 of them were able to give a response indicating they were able to read the problem, make sense of it, and determine there was not enough information to solve it.
While the results of this scenario are quite shocking, this kind of formulaic thinking when it comes to solving word problems is all too common.
In fact, when another mathematics educator tried a similar activity with her first graders, her results were just as astounding. (See the original post and video here. )
So, what’s the problem?
Using Keywords For Math Word Problems
Our students have been trained to look for math keywords, or clues, to what operation they are expected to perform to solve a math word problem. While I completely understand that teachers have perfected the use of keywords over the years in order to provide a strategy that would prove successful both in the classroom and on standardized tests, the use of keywords does not require students to think critically about a problem or allow them to make sense of the situation.
On a recent search in Pinterest, I was not surprised to find a plethora of pins related to using keywords for math word problems. The picture below shows a list of all the keywords that I found– many of which, I disagree with the placement or inclusion of.
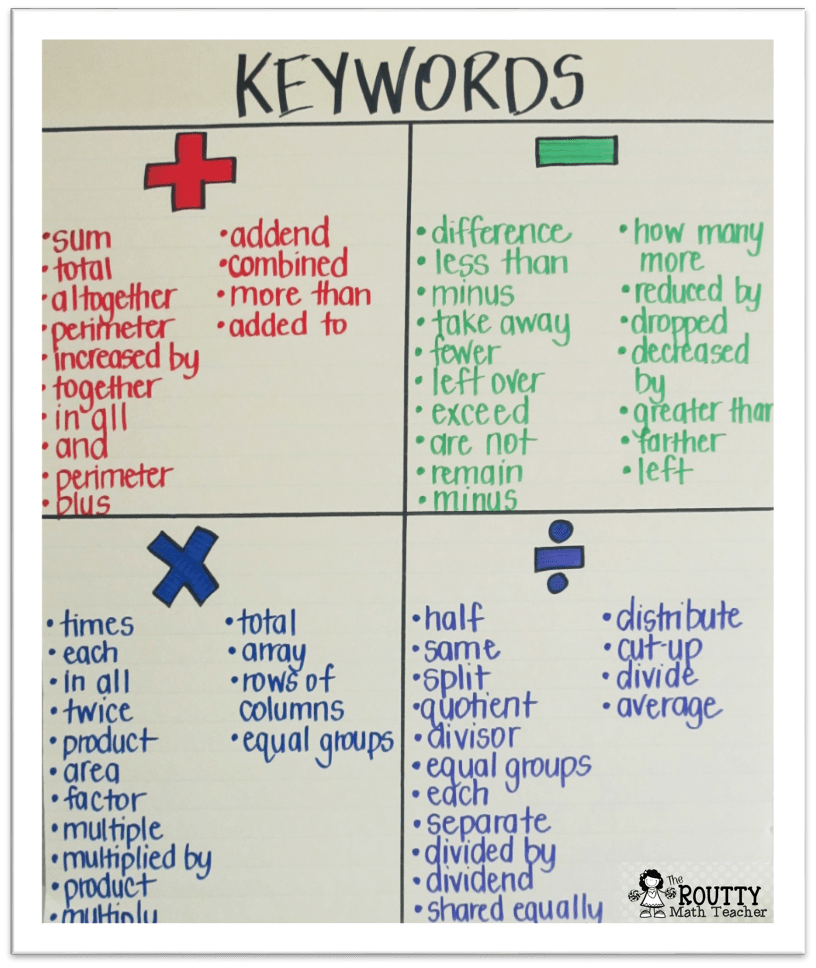
As a teacher, I can’t imagine what it would feel like to help my students memorize all of these terms. How are they going to learn them– with a weekly quiz?
I think not.
Why Not Keywords?
But using keywords for math word problems works just fine for me you say?
Van de Walle and Lovin (2006) and Van de Walle, Karp, and Bay-Williams (2012) offer four reasons to remove the use of keywords from our work with students:
1. Keywords can be Dangerous!
Many authors and resource creators use keywords in ways that differ from the way students expect them to be used which leads students to an incorrect solution strategy pathway. Add to that the use of multiple-meaning words and our students can become quickly overwhelmed and confused.
Consider the following problem: Julie left $9 on the table. Her brother left $6 on the table. How much money was left on the table? Use of the word “left” might indicate to some that the solution to this problem is obtained with subtraction; however, this is an addition situation because two quantities are being joined together.
(Find more “Keyword Fails” here.)
2. Use of Keywords Misses the Big Picture
The use of math keywords focuses on looking at the words in isolation and not in the context of the problem.
“Mathematics is about reasoning and making sense of situations” (Van de Walle & Lovin, 2006, p. 70); therefore, students should analyze the structure of the problems in the context not just dissect them for keywords.
When students begin to view problem situations in this way, they can identify the bigger picture and make connections between problem situations and the necessary solution strategy required to solve the problem.
3. What If There’s No Keyword?
Many problems, especially as students begin to advance to more sophisticated work, have no keywords.
Consider the following problem: Dominique had 10 flower petals. Four were green and the rest were orange. How many orange flower petals does Dominique have?
Because this problem does not contain keywords, students who rely on this approach will not have a strategy on which to rely, which will most likely result in a new word, like “rest” being added to the subtraction word list.
4. Will Keywords Support Students Long-Term?
While teachers in the younger grades claim to have great success using keywords for math word problems, the use of keywords does not work with more advanced problems or those with more than one step.
Therefore, students who do not attend to the meaning of a problem while solving it will be unsuccessful in completing the problem because they will miss the intermediate steps needed to lead to the final result.

Making Sense of Problems
The first Mathematical Practice Standard of the Common Core State Standards for Math describe mathematically proficient students as those who can:
- Explain the meaning of a problem
- Plan a solution pathway rather than jumping to a solution
- Continually check for reasonableness and ask, “Does this make sense?”
These three skills are essential to solving math word problems successfully.
But, how do we help students develop them?
Using Tricks To Replace Thinking
Tina Cardone, the author of Nix the Tricks, a guide to avoiding non-conceptually developmental short-cuts, suggests having students think about the words of the problem as a whole and focus on what is happening in the problem in context.
Students can accomplish this by visualizing the situation and creating a mental picture of the actions that are taking place. Once they understand the actions, students can then connect the actions to symbols.
After students have experience with a variety of problem situations, some patterns will begin to emerge as students begin to recognize recurring themes, such as joining, part-part-whole, separating, comparing, equal groups, sharing, and measuring.
Throughout the year, teachers can record the different situations students encounter on an anchor chart. Then replace that old, out-dated math keywords poster with the brand-spanking-new operation situations poster.

Want to know more about the operation situations and strategies to help with math word problems?
Download the free poster above using the form below and click here to learn more about strategies to help with math word problems.
Sound Off!
What strategies do you use to emphasize making sense of word problems with your students? Share your ideas in the comments section below.
References
- Common Core State Standards for Math
- https://gfletchy.com/2015/01/12/teaching-keywords-forget-about-it/
- http://nixthetricks.com/
- http://tjzager.com/2014/10/18/making-sense/
- Van de Wall, J. A., Karp, K. S., & Bay-Williams, J. M. (2012). Elementary and middle school mathematics: Teaching developmentally. Boston, MA: Pearson.
- Van de Wall, J. A. and Lovin, L. H. (2006). Teaching student-centered mathematics: Grades 3 – 5. Boston, MA: Pearson.




8 Responses
Love the Analyzing Word Problems poster!
Thank you SOOOOO very much. I always thought that lists of key words were incomplete and had so much crossover … and needed to be used in context. You have combined all of this in a clear and concise way. LOVE IT!
Hi Patricia!
I’m so glad you found the post useful!
~ Shametria
Hi. As a non math teacher,I really like this approach. Word problems were the hated vegetable that went with a main course I hated and couldn’t cut.
I was disappointed, though,that so many links didn’t work. I’m not sure how old the post is, so that may be the problem.
But thanks for teaching me to teach them.
Hi Diana!
I’m so glad you found the post helpful! I went through the post and all the links work; however, you may have read it at a time when I was updating the connecting posts and they were in draft form. My apologies about that. All the links do work though, so I encourage you to take another look. If you have any questions, please contact me at [email protected]. Thank you!
~ Shametria
What about EL learners? I have third grade newcomers who have zero language and have to work through word problems.
Interesting concept and makes sense… I tell my students to think about the action that is taking place to help them determine the operation needed.
Hi LaChone!
Love that you don’t focus on keywords– such a gamechanger!
Shametria